Technical data
The type of area can be added in the section Parameters - Areas - Manage area types. The newly created area is subsequently displayed under the overview of floor areas.
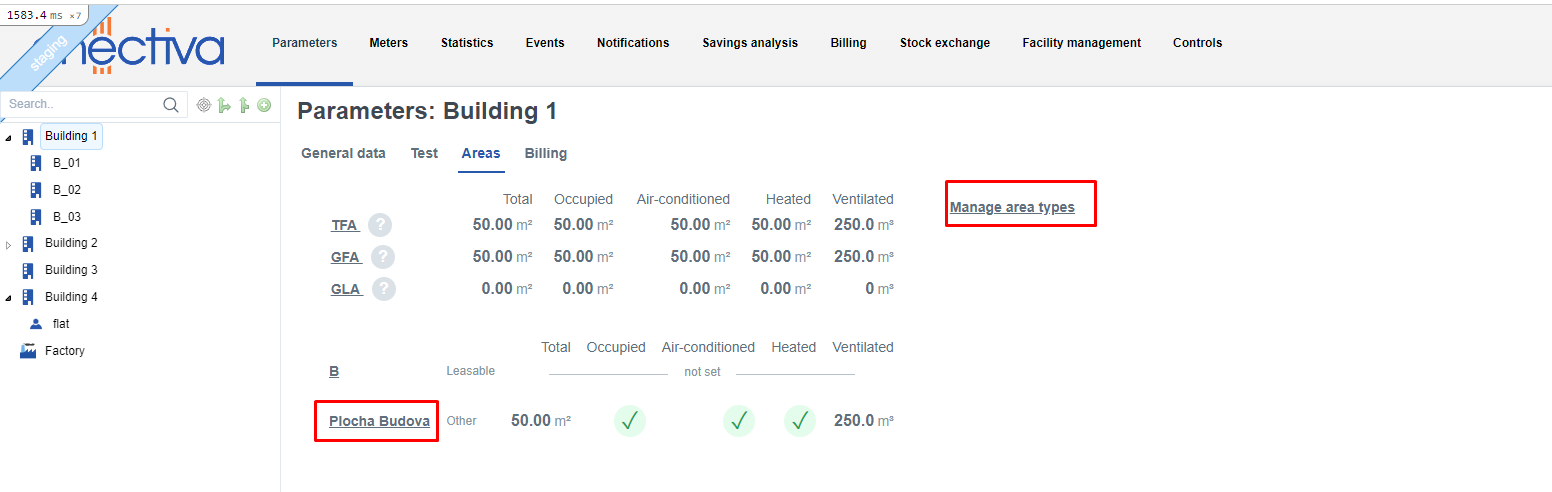
Technical data is used to facilitate comparison of consumption between different objects in the Statistics section - by clicking on the required floor area and the table for setting the technical data will open.
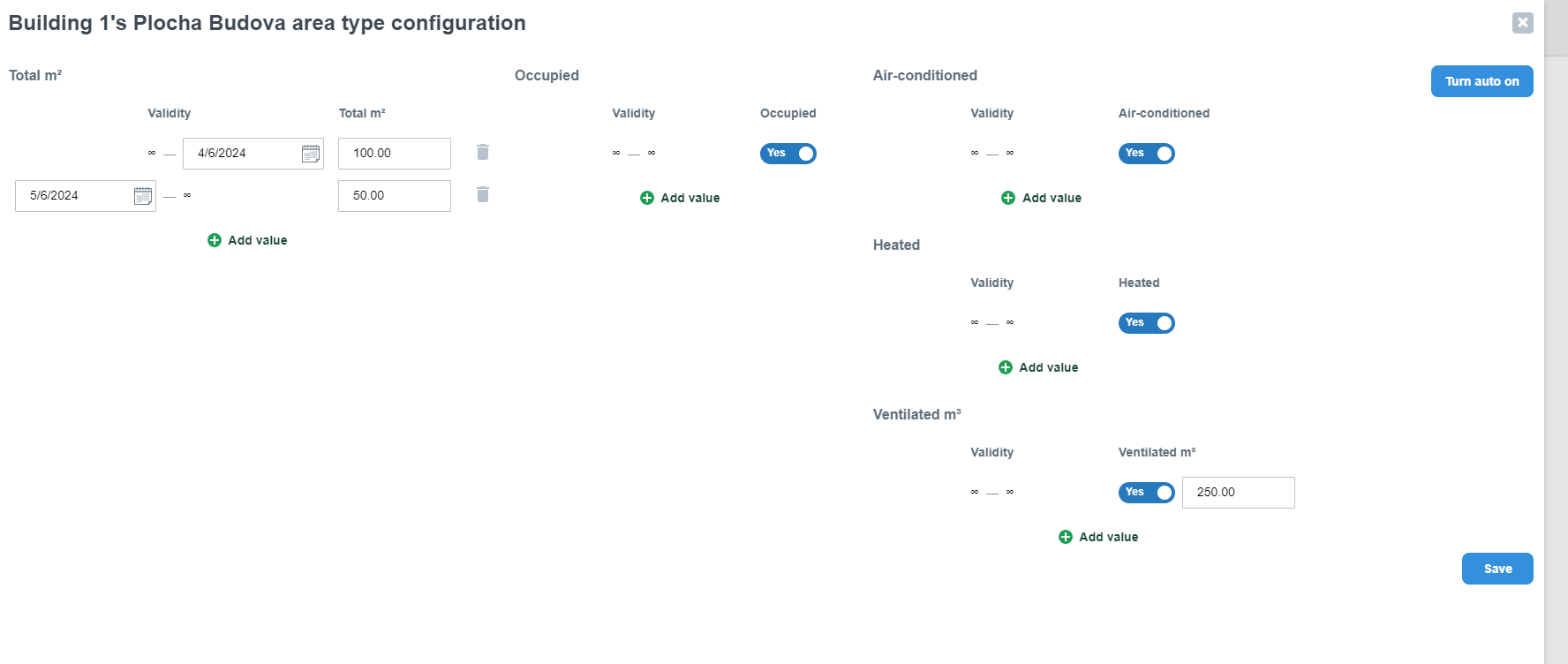
In this section it is possible to enter the parameters of the total area. More specifically how many square meters are cooled, heated and finally the total HVA Cvolume, more specifically what volume of air is treated by the HVAC.
In the Energy section, the types and parameters of circuit breakers are set. This data must be filled in to automatically calculate the cost of electricity according to the Price Lists. Reserved capacity and power input are used to set the wholesale customers' prices. To learn more about the price lists, see the Price Lists category.
Degrees days
The section on Dayrates is devoted to how energy is used in relation to dayrates.
Degree days are a unit that measures the need for heating or cooling between the average differential outdoor temperature and the target indoor temperature. There are two types of degree days:
Heating Degree Days (HDD) - for direct measurement of heating degree days > They show how much heating is needed
if the average outdoor temperature drops below a certain threshold.
Cooling Degree Days (CDD) - for direct measurement of cooling degree days > They show how much cooling is needed
if the average outdoor temperature exceeds a certain threshold.
HDD and CDD (heating degree days and cooling degree days) consist of two items.
- Internal temperature - defines the temperature that the device (boiler, air conditioner, etc.) is trying to reach.
- Reference temperature - defines the temperature at which the device starts the heating process.
HDD is then calculated using the following calculation:
"HDD" = "indoor temperature" - "average outside daily temperature"
If the average daily temperature is greater than the reference temperature, the HDD will be zero. This is due to the fact that the device is not operating (not heating) in this case.
= It is calculated as the difference between the target temperature (e.g. 20 °C) and the average outdoor temperature, if this outdoor temperature is lower than the threshold temperature (e.g. 15 °C).
- Example: Target temperature 20 °C, average outdoor temperature 10 °C -> HDD = 10
CDD is calculated using the following calculation:
"CDD" = "average outside daily temperature" - "reference temperature"
If the average outside daily temperature is lower than the reference temperature (for CDD), the CDD will be zero. In this case the device will not operate again.
= It is calculated as the difference between the average outdoor temperature and the target temperature if the outdoor temperature is higher than the threshold temperature.
- Example: Target temperature 20 °C, average outdoor temperature 30 °C -> CDD = 10
The average outside temperature is calculated using the measured outside temperature data series. Another option is to use data series that accurately measure HDD or CDD values. You can learn more about data series in the relevant chapter Data series.
Virtual Degree Days (vHDD and vCDD)
Virtual Degree Days (vHDD and vCDD) are available as separate data series. These series allow users to monitor heating
and cooling needs across different types of objects (buildings, factories, etc.).
- Virtual Degree Days can be assigned to multiple objects, with each object having at most one vHDD and one vCDD data series.
- Users can assign Degree Days to entities outside of their current subtree.
Management of vHDD and vCDD Data Series
- When creating a new data series for vHDD or vCDD, the user selects the outdoor temperature, which is linked to these Degree Days.
- These data series are stored in the system as historical records, allowing long-term tracking.
- The outdoor temperature cannot be deleted if it is already linked to Degree Days.